
Can Vitamin B12 Deficiency Be a Sign of Cancer?

Understanding the Link Between Vitamin B12 Deficiency and Cancer
Vitamin B12 deficiency is more than just a nutritional shortfall—it may, in some contexts, hint at deeper health issues. When asking, can vitamin B12 deficiency be a sign of cancer, it’s essential to understand that while B12 deficiency isn’t a definitive cancer marker, it can occasionally be associated with cancer, especially those affecting the gastrointestinal tract. Pernicious anaemia, a common cause of B12 deficiency, has been linked to an increased risk of stomach cancer due to its effect on the stomach lining.
Around 1 in 5 adults over 60 in the UKare deficient in vitamin B12, which can lead to fatigue, nerve issues, and cognitive decline if left untreated.
Moreover, studies have noted that individuals with certain cancers, such as colorectal or pancreatic cancer, often present with low B12 levels. This suggests a possible, though not conclusive, association. Repeatedly asking can vitamin B12 deficiency be a sign of cancer reflects a need for more research, but current findings support ongoing awareness.

The Role of B12 in Cellular Health
Vitamin B12 is vital for healthy DNA synthesis and cell replication. A deficiency can lead to the production of unusually large red blood cells, which may mask or mimic other health issues, including some types of cancer. This overlapping symptom profile can confuse diagnoses and delay treatment. Since B12 also supports immune function, low levels may impair the body’s defence against malignant cells. Therefore, the question can vitamin B12 deficiency be a sign of cancer often arises in clinical evaluations, especially when other symptoms align.

How Long to Recover from Vitamin B12 Deficiency
Recovery from B12 deficiency depends on multiple factors, including severity and treatment. If the deficiency is identified early and treated with injections or high-dose supplements, patients often see improvements in energy within days. However, complete recovery, especially from neurological symptoms, can take several months. Many ask, how long to recover from vitamin B12 deficiency and the answer varies, but with consistent care, most people see substantial improvement within 6 to 12 months. This timeframe underscores the importance of early detection when considering whether vitamin B12 deficiency could be a sign of cancer.
Factors That Affect Recovery Duration
Recovery from vitamin B12 deficiency can be influenced by:
- Severity of the deficiency
- Underlying cause, like pernicious anaemia or absorption issues
- Type of treatment, such as oral versus injectable B12
- Overall health and compliance with the regimen
How Long Does It Take B12 to Start Working?
Many patients start to feel better within a few days after beginning B12 treatment, especially if using injections. Oral supplements may take longer, often showing results in a few weeks. For those asking how long does it take B12 to start working, it’s usually noticeable within the first fortnight, but the full spectrum of benefits may unfold over months.
How Long After Starting Vitamin B12 Will I Feel Better?
Patients often wonder how long after starting vitamin B12 will I feel better. While energy and mood improvements may begin in days, neurological symptoms might take longer to resolve. People with prolonged deficiencies may need several months to feel fully restored. Monitoring this progression helps doctors decide whether additional evaluations are needed, especially if there’s concern about whether a vitamin B12 deficiency might be a sign of cancer.
What Should Your B12 Level Be?
Knowing what should your B12 level be is crucial in both identifying deficiencies and monitoring recovery. A normal B12 range is typically 200-900 pg/mL. Levels below 200 pg/mL are considered deficient. However, symptoms can still occur at borderline levels (200-300 pg/mL), especially in vulnerable populations. These ranges are key in the broader discussion of whether vitamin B12 deficiency can be a sign of cancer, particularly when seen in the context of other health anomalies.

Does B12 Deficiency Cause Hair Loss?
Hair loss is a concern many associate with nutrient deficiencies. So, does B12 deficiency cause hair loss? The answer is yes, potentially. Since B12 plays a role in red blood cell formation, a lack of it can impact oxygen delivery to hair follicles, leading to thinning. Addressing B12 levels through diet or supplementation may help restore hair health, though it’s one piece of the puzzle. Persistent hair loss, alongside fatigue and neurological signs, might prompt deeper investigation, including the possibility that vitamin B12 deficiency could be a sign of cancer.
Ongoing Monitoring and Nutrient Balance
To ensure effective treatment and recovery from B12 deficiency, ongoing blood tests and clinical evaluations are necessary. This not only helps answer questions like how long does it take B12 to start working or how long to recover from vitamin B12 deficiency, but also alerts clinicians to any other health concerns. Given how symptoms of B12 deficiency overlap with those of certain cancers, persistent deficiencies warrant thorough assessment to explore whether they could indeed signal something more serious, like cancer.
| GET 20% OFF | Use Code:
B12-DEFICIENT
-
Product on sale
 Vitamin B12 Max Strength 60 PatchesOriginal price was: £39.99.£15.99Current price is: £15.99.
Vitamin B12 Max Strength 60 PatchesOriginal price was: £39.99.£15.99Current price is: £15.99.

Can Vitamin B12 Deficiency Be Misdiagnosed?
Vitamin B12 deficiency can often be misdiagnosed because its symptoms mimic other common conditions such as depression, thyroid dysfunction, and chronic fatigue syndrome. These overlaps make it difficult to determine if a person is just deficient in B12 or if there is a more serious underlying condition. This is particularly important when considering questions like can vitamin B12 deficiency be a sign of cancer, as early misinterpretation could delay necessary diagnostics. Symptoms such as fatigue, memory lapses, and nerve tingling are shared across several illnesses. Misdiagnosis can mean the deficiency—and possibly other conditions—go unaddressed for too long, increasing the risk of complications.
Why Diagnosis Can Be Tricky
One major challenge in diagnosing a B12 deficiency accurately is that the body can store vitamin B12 for years, masking symptoms until levels drop drastically. Moreover, even when serum B12 appears normal, functional deficiency may still exist if the vitamin isn’t properly absorbed or utilised by the body. This misalignment can prompt questions like what should your B12 level be and whether B12 levels alone are a good indicator of health. Functional markers like MMA and homocysteine can help clarify the picture.

Can You Have Too Much Vitamin B12?
Although rare, some individuals may present with very high vitamin B12 levels. While excess intake is usually excreted safely due to B12 being water-soluble, unusually high levels can occasionally signal hidden health issues like liver disease or certain cancers. This raises an interesting consideration in the context of can vitamin B12 deficiency be a sign of cancer, because both low and high levels could warrant further investigation. It reinforces the importance of interpreting B12 results within a broader clinical context.
When to Be Concerned About High Levels
It’s essential not to self-prescribe or over-supplement with B12, especially if you already suspect a deficiency or experience signs linked to underlying disease. Instead, discuss dosage and monitoring with a healthcare professional to avoid overcorrection, particularly when symptoms overlap with conditions like cancer.
Is Vitamin B12 Deficiency Reversible?
Thankfully, most cases of vitamin B12 deficiency are reversible if caught early. This is particularly encouraging for those asking “how long to recover from vitamin B12 deficiency” or how long after starting vitamin B12 will I feel better. With prompt treatment—either through oral supplements or injections—energy levels, cognition, and mood often improve within weeks. More persistent symptoms, especially neurological ones, can take longer but tend to recover over time with consistent supplementation.
Recovery Outlook
The timeline for feeling better depends heavily on the individual, but many report positive changes within the first month. For those wondering “how long does it take B12 to start working,” initial improvements may be felt in a few days to a week. However, full recovery, especially from long-standing symptoms, can take six months or more.
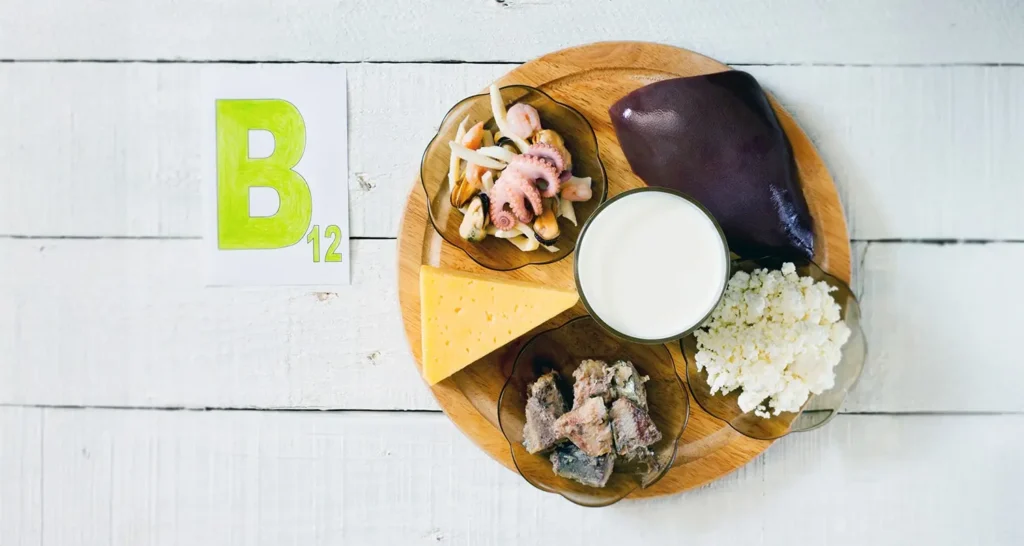

What Foods Are High in Vitamin B12?
Ensuring an adequate intake of B12 through diet can prevent deficiency and its associated complications. Foods rich in B12 include beef liver, clams, sardines, and fortified cereals. Including these foods regularly is key for those asking what should your B12 level be or managing ongoing supplementation plans. For vegans and vegetarians, fortified plant milks and nutritional yeast are essential dietary sources.
Top Sources of Vitamin B12:
| Food Source | B12 Content (mcg per serving) |
|---|---|
| Beef liver (3 oz) | 70.7 |
| Clams (3 oz) | 84.1 |
| Fortified cereal | 6.0 |
| Salmon (3 oz) | 4.9 |
| Nutritional yeast | 2.4 |
| Milk (1 cup) | 1.2 |
Can Stress Cause B12 Deficiency?
Stress, while not a direct cause, can contribute to vitamin B12 deficiency by influencing dietary habits, reducing nutrient absorption, and altering stomach acid production. In stressed individuals, it’s not uncommon to see lower B12 levels, raising concerns like can vitamin B12 deficiency be a sign of cancer if symptoms such as chronic fatigue or memory problems arise alongside other signs.
Managing Stress for Better Nutrient Absorption
To counter the potential impact of stress on B12 absorption, adopting stress-reducing habits such as regular exercise, mindful eating, and adequate sleep is crucial. These habits also complement B12 supplementation and can accelerate how long after starting vitamin B12 one will feel better.
-
Product on sale
 Anxiety Support Oral DropsOriginal price was: £59.99.£24.99Current price is: £24.99.
Anxiety Support Oral DropsOriginal price was: £59.99.£24.99Current price is: £24.99.
Who Is Most at Risk for Vitamin B12 Deficiency?
At-risk populations include older adults, those with gastrointestinal disorders, vegans, and individuals on medications like PPIs or metformin. These groups often ask, how long to recover from vitamin B12 deficiency or question what should your B12 level be, highlighting the need for proactive testing and personalised care.
Identifying Risk Early
Routine screening in high-risk groups allows for early intervention and avoids complications. For some, ongoing supplementation may be required to maintain adequate levels and avoid symptoms that mimic more serious conditions, which can lead people to wonder whether their B12 issues could signal cancer.
Can Vitamin B12 Supplements Interact with Medications?
While generally safe, B12 absorption can be hindered by long-term use of medications like metformin and PPIs. Understanding these interactions is essential to ensuring supplementation is effective and timely for those managing chronic illness or asking, how long does it take B12 to start working?
Staying Safe with Supplement Use
Always discuss supplements with your doctor to avoid interactions and track progress, especially when addressing complex symptoms potentially tied to chronic conditions or exploring whether vitamin B12 deficiency might relate to cancer.

Does B12 Deficiency Affect Mental Health?
Yes, low B12 levels can lead to symptoms like anxiety, mood swings, and even depression. This mental health link is vital when asking does B12 deficiency cause hair loss or other signs that seem unrelated but could be systemic effects of deficiency. Reversing these symptoms often begins with restoring proper B12 levels.
Supporting Cognitive Function
Mental clarity, memory, and focus often improve after B12 treatment begins. This connects back to questions such as how long after starting vitamin B12 will I feel better—many report sharper thinking and reduced brain fog within weeks.

Can Children Have Vitamin B12 Deficiency?
Children, particularly those in vegan households, can develop B12 deficiency. Symptoms may include poor concentration, fatigue, and stunted growth. It’s essential to address these early, especially if concerns arise about long-term impacts or if parents are asking, can vitamin B12 deficiency be a sign of cancer in rare but severe cases.
Monitoring in Early Life
Regular check-ups and supplementation for at-risk children can prevent developmental delays and improve outcomes significantly.

Can B12 Deficiency Affect Sleep?
Yes, B12 plays a role in melatonin production, which regulates sleep cycles. A deficiency may lead to insomnia or unrestful sleep. For those asking how long does it take B12 to start working, better sleep is often one of the first signs of improvement.
Optimising Sleep Naturally
Improving B12 levels through diet or supplements and practising good sleep hygiene can help reset sleep patterns. This is particularly useful for those experiencing prolonged fatigue or questioning whether their symptoms might be linked to something more serious like cancer.
Vitamin B12 Supplements
-
Product on sale
 60 Vitamin B12 & Magnesium PatchesOriginal price was: £29.99.£16.99Current price is: £16.99.
60 Vitamin B12 & Magnesium PatchesOriginal price was: £29.99.£16.99Current price is: £16.99. -
Product on sale
 30 Iron & Vitamin Patches
30 Iron & Vitamin Patches
Vitamin C, A & B12Original price was: £39.99.£19.99Current price is: £19.99. -
Product on sale
 30 Vitamin B12 & Folic Acid PatchesOriginal price was: £39.99.£19.99Current price is: £19.99.
30 Vitamin B12 & Folic Acid PatchesOriginal price was: £39.99.£19.99Current price is: £19.99.
Can Vitamin B12 Deficiency Be a Sign of Cancer?
Frequently Asked Questions:
Does low vitamin B12 indicate cancer?
Low vitamin B12 doesn’t directly indicate cancer, but chronic deficiencies may be observed in certain cancers like gastric or pancreatic cancer, often due to impaired absorption. While this link exists, it’s not a diagnostic tool for cancer, and many non-cancerous issues cause B12 deficiency.
More commonly, low B12 is tied to conditions like pernicious anaemia, intestinal disorders, or poor dietary intake. A healthcare professional should investigate any B12 deficiency thoroughly before drawing conclusions.
What causes low B12 in females?
Females may experience low B12 due to diet, especially vegetarian or vegan habits, since B12 is found mainly in animal products. Digestive disorders, hormonal shifts, and medications like birth control or antacids can also impair absorption.
Pregnancy increases the demand for B12, making deficiency more likely if intake or absorption is insufficient. It’s important to monitor levels during these stages to support overall wellbeing.
Can low B12 make your joints hurt?
While joint pain isn’t a classic symptom, B12 deficiency can cause nerve-related pain that mimics joint discomfort. It may be felt as tingling, numbness, or burning pain that radiates through limbs.
The root cause is nerve damage or dysfunction rather than inflammation of the joints. If persistent joint-like pain occurs, it’s worth checking B12 levels and overall nerve health.
What is the fastest way to fix B12 deficiency?
Rapid correction of B12 deficiency typically involves high-dose oral supplements or addressing the root cause, such as improving dietary intake. Foods rich in B12 like eggs, meat, and dairy are effective if digestion is normal.
For those with absorption issues, B12-fortified foods or liquid supplements may be better absorbed. Regular testing ensures treatment is working effectively.
Should I be worried if my B12 is low?
Low B12 can become a serious concern if left untreated. It can affect brain function, red blood cell formation, and nerve health, potentially leading to irreversible damage over time.
Early signs like fatigue or brain fog may seem minor but can progress. It’s best to address any deficiency promptly with medical guidance.
What organ is affected by B12 deficiency?
The nervous system and brain are especially vulnerable to low B12, with symptoms like memory issues, mood disturbances, or coordination problems. The bone marrow, which produces blood cells, is also affected.
Without enough B12, red blood cells can’t form properly, leading to anaemia. The stomach and intestines may also be involved if absorption is impaired.
What are the worst symptoms of B12 deficiency?
Severe B12 deficiency may lead to neurological damage, including numbness, balance issues, and cognitive impairment. In extreme cases, it can mimic dementia.
Other serious signs include palpitations, shortness of breath, glossitis (inflamed tongue), and depression. Long-term deficiency without treatment can cause irreversible damage.
Does B12 affect bowel movements?
Yes, B12 can influence digestion. Deficiency might slow gastrointestinal function, contributing to constipation or other digestive complaints.
B12 plays a role in energy metabolism, so low levels may indirectly lead to sluggish bowel activity. Correcting the deficiency often improves these symptoms.
How long does it take to recover from vitamin B12 deficiency?
Recovery time varies depending on severity. Some people feel better within days of starting supplements, while full correction may take weeks to months.
Neurological symptoms may take longer to resolve, and if the deficiency is prolonged, some damage may be permanent. Regular monitoring is key during recovery.
What are the facial signs of B12 deficiency?
Facial signs can include pale or jaundiced skin and a smooth, swollen tongue. Some individuals may also develop mouth ulcers or a tingling sensation in the face.
These symptoms occur due to blood cell changes and nerve involvement, which are both affected by B12 levels. They’re often accompanied by general fatigue or weakness.
Can low B12 feel awful?
Yes, low B12 can cause a wide range of symptoms that make you feel terrible. Common complaints include extreme tiredness, brain fog, irritability, and dizziness.
As it progresses, more debilitating effects like numbness or depression may appear. People often report not feeling like themselves and feeling worse over time if untreated.
How soon will I feel better after taking vitamin B12?
Many people begin to notice improvements in energy and mood within a few days to a week of starting B12 supplements, especially if they were very low.
However, full recovery of neurological symptoms or anaemia can take longer, often several weeks or months depending on the severity and consistency of treatment.
What happens if your B12 is low for too long?
Prolonged B12 deficiency can lead to irreversible nerve damage, memory loss, and mobility issues. In some cases, it can cause psychiatric symptoms or permanent neurological changes.
It can also lead to megaloblastic anaemia, where blood cells are abnormally large and function poorly. Long-term deficiency requires medical attention to avoid lasting harm.
What cancers are linked to B12 deficiency?
Research suggests associations between B12 deficiency and certain gastrointestinal cancers, such as stomach and pancreatic cancer. These links are typically due to absorption problems caused by the cancer, rather than B12 causing cancer directly.
For instance, chronic atrophic gastritis, which reduces B12 absorption, can increase stomach cancer risk. However, these links are indirect and not widely generalised.
Can lack of B12 affect your eyes?
Yes, B12 deficiency can potentially cause vision problems. One rare but serious effect is optic neuropathy, where the optic nerve is damaged, leading to blurred or disturbed vision.
This usually occurs in severe, untreated cases, and may be reversible if caught early. Regular eye checks and timely treatment help prevent this complication.
Is B12 deficiency serious?
Yes, it can be quite serious if ignored. While it starts with mild fatigue or cognitive changes, prolonged deficiency can lead to irreversible damage to nerves or the brain.
It’s also linked to cardiovascular risks and poor mental health. Fortunately, it’s treatable if caught early, so it’s crucial to act on symptoms promptly.
Can lack of B12 cause neck pain?
B12 deficiency may contribute to musculoskeletal pain, including in the neck, but this is typically due to nerve irritation rather than direct muscle or joint issues.
Neuropathy caused by low B12 can create pain patterns that radiate to the neck and shoulders, especially if accompanied by fatigue or numbness.
Can you live with low B12?
You can live with low B12 for a while, but quality of life may diminish as symptoms worsen. Chronic fatigue, mood swings, and memory issues are common with prolonged deficiency.
Left untreated, the damage may become permanent. Lifelong supplementation or diet changes may be necessary in some cases to maintain health.
What cancer causes vitamin deficiency?
Gastrointestinal cancers, such as stomach or colon cancer, may impair the body’s ability to absorb nutrients like B12, iron, or folate. This can lead to chronic deficiencies even if dietary intake is sufficient.
These deficiencies often result from tumour-related inflammation or surgical removal of parts of the digestive tract. Nutrient absorption should be monitored in patients with such conditions.
Why would your B12 be low?
There are many reasons, from dietary gaps to medical issues. Vegans and vegetarians often lack adequate B12 sources. Digestive conditions like coeliac or Crohn’s disease can impair absorption.
Other causes include medications, alcohol overuse, ageing, and autoimmune disorders like pernicious anaemia. Identifying the cause is key to effective treatment.
How has B12 deficiency ruined my life?
Many individuals report major disruptions in their daily lives due to chronic fatigue, cognitive fog, anxiety, and nerve pain caused by low B12. These symptoms can interfere with work, relationships, and mental health.
Recovery is possible with the right diagnosis and treatment. Awareness and early testing are essential to avoid long-term complications and regain quality of life.
Which fruit is rich in vitamin B12?
Fruits are not natural sources of vitamin B12. This nutrient is found primarily in animal products like meat, eggs, dairy, and fish. However, some plant-based products, like fortified cereals or plant milks, have added B12.
People on a plant-based diet should consider these fortified foods or supplements to maintain healthy B12 levels. Regular monitoring is recommended.
What does B12 acne look like?
In rare cases, high doses of B12 supplements can trigger acne-like breakouts, often around the chin and jawline. This is believed to be due to bacteria reacting to excess B12.
The acne is usually red, inflamed, and may resemble hormonal acne. Reducing supplementation or switching forms often resolves the issue.











